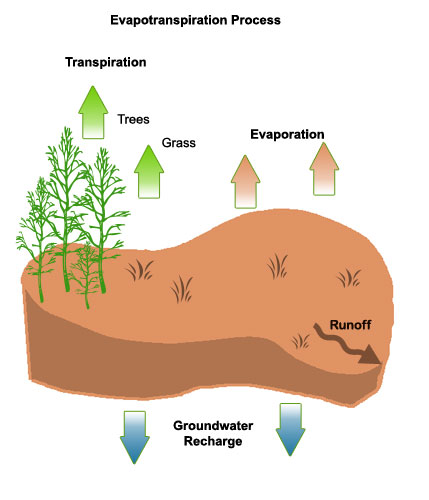
| The term Evapotranspiration (ET) combines the concepts of evaporation (E) from soil and plant surfaces with transpiration (T) from plant leaves to describe the total water escaping from a crop to the air. Evapotranspiration increases with: higher air temperature, more solar (light) energy, lower humidity, and faster wind speed. Evapotranspiration is often referred to as "crop water use" because the two processes are so closely entwined and difficult to separate. Irrigation Scheduling:The Water Balance Approach, CSU Fact Sheet 4.707
AGRIMET Irrigation Guide, USBR
ET Primer, Kansas State University
Using ET Reports for Center Pivot Irrigation Scheduling, Kansas State University
Using ET Reports for Furrow Irrigation Scheduling, Kansas State University
Using Modified Atmometers (ET gage) for Irrigation Management, University of Nebraska
ET Irrigation Scheduling, Oregon State University
|

